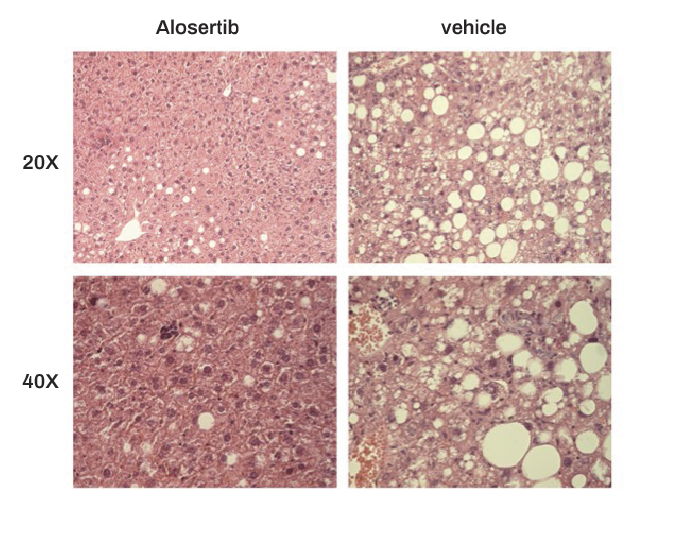
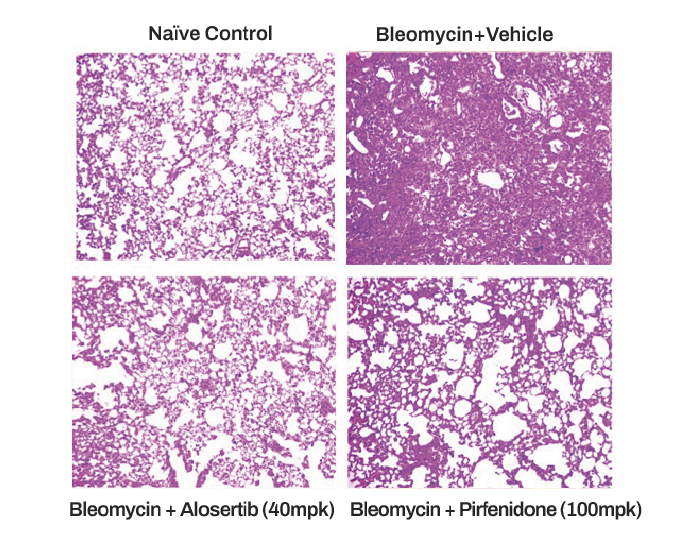
To offer the best experiences, we use technologies such as cookies to store and/or access device information. Consent to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Failure to consent, or withdrawal of consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Storage or technical access is strictly necessary for the legitimate purpose of allowing the use of a specific service explicitly requested by the subscriber or user, or for the sole purpose of carrying out the transmission of a communication over an electronic communications network. .
Technical storage or access is necessary for the legitimate purpose of storing preferences not requested by the subscriber or user.
Storage or technical access that is used exclusively for statistical purposes.
El almacenamiento o acceso técnico que se utiliza exclusivamente con fines estadísticos anónimos. Sin un requerimiento, el cumplimiento voluntario por parte de tu proveedor de servicios de Internet, o los registros adicionales de un tercero, la información almacenada o recuperada sólo para este propósito no se puede utilizar para identificarte.
El almacenamiento o acceso técnico es necesario para crear perfiles de usuario para enviar publicidad, o para rastrear al usuario en una web o en varias web con fines de marketing similares.